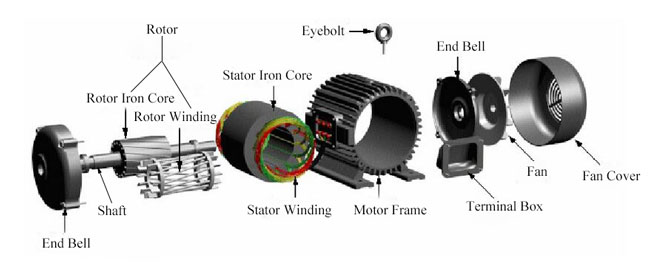
1. Stator
Stator is a fixed part of induction motor, consisting of stator iron core, stator windings andmotor frame.
Stator iron core
As a part of the motor magnetic circuit, it is installed inside the motor frame. It is a hollow cylinder, outer wall of which is connected to the motor frame. And the stator windings are placed in the slot of the iron core inside. In order to reduce the loss of iron core, the stator iron core is stacked up with 0.5 mm thick silicon steel sheets.
Stator winding
It is a part of the motor electric circuit, generating the rotating magnetic field by inducing three-phase alternating current. Stator windings are wound with insulated copper wires and embedded in the stator slot, which are separated by insulating material between the windings and the slot.
Motor frame
It fixes the stator core and stator windings and supports the rotor with two end bells. Meanwhile, it protects the electromagnet part of the entire motor and dissipates the heat generated during motor operation. The frame is typically made from iron or aluminum.
2. Rotor
Rotor is a rotating part of induction motor, including iron core, windings and shaft etc.
Rotor iron core
It is also a part of the magnetic circuit, generally stacked by silicon steels and fixed on the shaft.
Shaft
It plays a role of converting torque and support the rotor. It is generally made of medium carbon steel or alloy steel.
Rotor winding
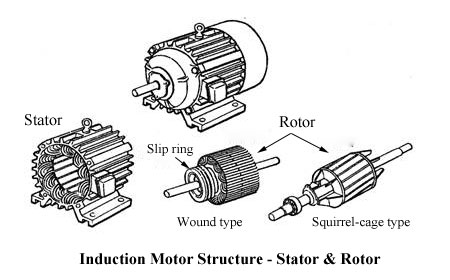
It produces induced current as cutting the stator magnetic field, and under the effect of the rotating magnetic field, it forces the rotor to rotate. According to the different structure, it can be divided into two types: squirrel-cage rotor and wound rotor.
The wound-type rotor windings can be connected into star or delta connection. In general, the small capacity rotor is connected into delta while the large and medium capacity one is connected into star. These three windings wire ends are connected to three slip rings fixed on the shaft by a set of electric brush. It can connect the external resistor to the rotor winding circuit. The purpose of string resistance is to improve the motor characteristics or adjust the rotate speed.
https://stepper011.jimdofree.com/2019/11/08/what-stepping-modes-does-a-stepping-motor-have/
https://c00alvin.blogrip.com/2019/11/07/how-do-you-control-and-run-a-stepper-motor/